In the era of digital transformation, safeguarding cloud infrastructure has become a mission-critical priority for government agencies and their partners. The Continuous Diagnostics and Mitigation (CDM) program, a cybersecurity initiative developed by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and administered by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), plays a pivotal role in defending federal networks. Designed to enhance the real-time visibility and security of cloud and on-premise systems, the CDM program empowers agencies to identify vulnerabilities, monitor threats, and mitigate risks continuously.
This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the continuous diagnostics and mitigation program, its phases, its role in cloud security, and how solutions like Kion help agencies achieve CDM compliance across complex cloud environments.
What Is the Continuous Diagnostics and Mitigation (CDM) Program?
The Continuous Diagnostics and Mitigation program is a U.S. government-led effort focused on bolstering cybersecurity across federal civilian departments and agencies. The initiative offers a suite of tools and capabilities that enable continuous monitoring, real-time diagnostics, and rapid threat mitigation for both traditional and cloud-based IT infrastructures.
Administered by CISA, the program aims to improve the overall cybersecurity posture by providing Chief Information Officers (CIOs) and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) with actionable data. This data is collected through integrated sensors and analytics tools that continuously assess vulnerabilities, suspicious behavior, and configuration issues. The CDM dashboard offers a centralized view, allowing agencies to prioritize and respond to the most critical risks promptly.
With the increased migration to cloud environments, the role of continuous diagnostics and mitigation has expanded to include governance, visibility, and protection across cloud service providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Objectives of the CDM Program
The CDM initiative serves as a framework for federal agencies and contractors to meet stringent cybersecurity mandates. The key goals of the program include:
- Reducing the attack surface across federal networks and cloud environments.
- Increasing visibility into network components, user activity, and data flows.
- Improving incident response and risk mitigation strategies.
- Streamlining FISMA (Federal Information Security Modernization Act) reporting and compliance efforts.
By implementing continuous diagnostics and mitigation, agencies are better equipped to manage risk, ensure compliance, and maintain trust in government systems.
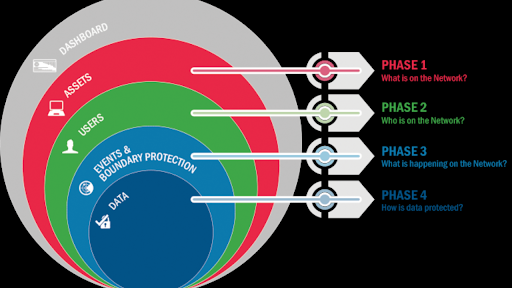
Why CDM Has Four Key Phases
To guide agencies through the process of securing their IT environments, CISA structured the continuous diagnostics and mitigation program into four well-defined phases. These phases help organizations take a step-by-step approach to assess, protect, and improve their cybersecurity posture.
Phase 1: What Is on the Network?
This phase focuses on asset management. Agencies are required to identify and inventory all hardware and software across their environments. The goal is to establish a clear understanding of what assets exist, how they are configured, and where vulnerabilities may reside.
Key capabilities include:
- Hardware Asset Management (HWAM)
- Software Asset Management (SWAM)
- Configuration Settings Management (CSM)
- Vulnerability Management (VUL)
Cloud-related questions to consider:
- What cloud resources exist in your environment?
- Who owns and manages these resources?
- Are configurations secure and compliant?
Understanding your inventory is the first step in applying continuous diagnostics and mitigation strategies effectively.
Phase 2: Who Is on the Network?
Phase 2 is about managing user identities and access control. Knowing who has access to which resources and what privileges they hold is vital in preventing unauthorized use.
Capabilities in this phase include:
- Privilege Management (PRIV)
- Trust Determination (TRUST)
- Credential and Authentication Management (CRED)
- Security Behavior Monitoring (BEHAVE)
Cloud-related questions:
- Which users have access to cloud assets?
- Are access levels aligned with the principle of least privilege?
This phase ensures that only the right people have the right access, a critical element in any continuous diagnostics and mitigation plan.
Phase 3: What Is Happening on the Network?
At this stage, real-time monitoring becomes the focus. Agencies must understand how systems and users behave to detect anomalies, malicious activity, or breaches.
Key capabilities:
- Managing Events (MNGEVT)
- Ongoing Monitoring and Improvement (OMI)
- Designing Security into Systems (DBS)
- Boundary Protection (BOUND)
- Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM)
Cloud-specific questions:
- How is data flowing through the cloud?
- Are these flows monitored continuously?
This phase ensures that continuous diagnostics and mitigation efforts are not static but adapt to evolving threats and infrastructure changes.
Phase 4: How Is Data Protected?
The final phase zeroes in on data security. Agencies must implement protections that ensure data is encrypted, properly classified, and resilient against loss or leakage.
Core capabilities:
- Data Discovery and Classification (DISC)
- Data Protection (PROT)
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Breach and Spillage Mitigation (MIT)
- Information Rights Management (IRM)
Questions to answer:
- What safeguards are in place to protect sensitive data?
- Are cloud resources continuously monitored to detect risks?
These protections complete the full continuous diagnostics and mitigation cycle, ensuring end-to-end coverage.
Common Challenges in Cloud Security
As agencies increase their reliance on cloud platforms, challenges like inconsistent governance, unclear risk ownership, and insufficient access controls become more prominent. Agencies may secure individual elements (such as virtual machines or storage) but miss the bigger picture of securing the entire infrastructure.
That’s where a platform like Kion becomes crucial.
How Kion Supports CDM for Cloud Infrastructure
Kion is a DHS-approved solution designed to help agencies achieve full compliance with continuous diagnostics and mitigation requirements across all four CDM phases. Kion provides a centralized platform that integrates cloud governance, compliance enforcement, access control, and financial management.
Kion’s key benefits:
- Automated account creation and provisioning
- Policy enforcement and access management across clouds
- Continuous compliance checks for NIST 800-53, 800-171, CIS Benchmarks, and more
- Centralized dashboard for reporting and budget enforcement
- Real-time scanning and auditing for vulnerabilities
Whether you’re managing AWS, Azure, or GCP environments, Kion delivers a single pane of glass solution that aligns with the continuous diagnostics and mitigation framework.
Use Kion to Excel with the CDM Program
Adopting continuous diagnostics and mitigation is not just a regulatory requirement—it’s a strategic necessity. With the help of robust tools like Kion, federal agencies and their partners can maintain a proactive security posture, quickly adapt to emerging threats, and ensure regulatory compliance with ease.
If you’re ready to strengthen your cloud infrastructure and align with CDM mandates, Kion offers the tools, insights, and automation needed to succeed. Schedule a demo today and take the first step toward comprehensive, scalable cloud security.
FAQs:
What is the purpose of the Continuous Diagnostics and Mitigation program?
The continuous diagnostics and mitigation program is designed to improve the cybersecurity posture of federal civilian agencies by providing tools and capabilities for real-time risk detection, analysis, and mitigation.
Who manages the CDM program?
The program is managed by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
How many phases are there in the CDM program?
There are four phases:
- What is on the network?
- Who is on the network?
- What is happening on the network?
- How is data protected?
Why is CDM important for cloud security?
Continuous diagnostics and mitigation helps agencies manage cloud security by ensuring real-time visibility, access control, policy enforcement, and compliance with federal cybersecurity standards.
What role does Kion play in the CDM process?
Kion is a DHS-approved platform that automates CDM compliance for cloud resources by managing access, enforcing policies, providing financial and security reporting, and supporting continuous compliance across multi-cloud environments.
Stay in touch to get more updates & news on Contact Help!